Your Location:Home > Products > Organic Chemistry > Methylmagnesium chloride
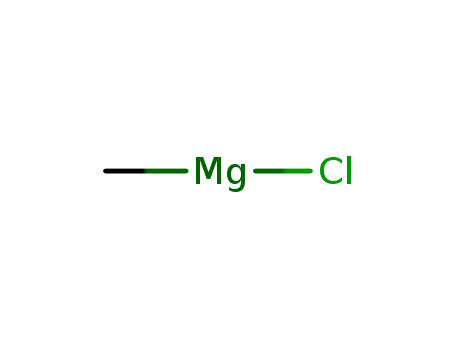
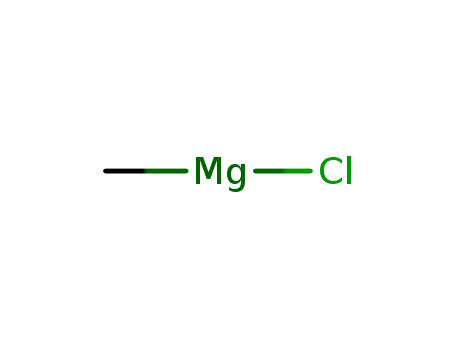
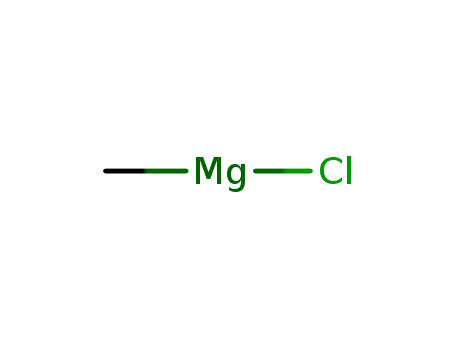
CasNo: 676-58-4
MF: CH3 Cl Mg
Appearance: dark brown solution
|
Description |
Methylmagnesium chloride is typically available as a solution in tetrahydrofuran (THF). Its unique properties and sensitivity to moisture make it essential to handle it with care, but when used correctly, it can be a powerful tool in the creation of various organic compounds in the field of chemistry. |
|
Uses |
Methylmagnesium chloride plays a pivotal role in organic chemistry, particularly as a methylation reagent. It is employed for introducing methyl (CH3) groups into organic compounds. Methylmagnesium chloride is used not only as a methylation reagent but also as a Grignard reagent and an alkylating agent. It functions as an alkylmagnesium halide and is considered a one-carbon compound, making it a valuable tool in various organic synthesis reactions. |
|
Hazard |
Flammable, dangerous fire and explosionrisk. |
InChI:InChI=1/CH3.ClH.Mg/h1H3;1H;/q;;+1/p-1/rCH3Mg.ClH/c1-2;/h1H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
Pulsed and continuous (or direct) currents were used for the electrodeposition of magnesium from methylmagnesium chloride solution. The electrochemical results showed that the protection of the steel substrate against corrosion was better with the magnesium deposit obtained by pulsed electrodeposition process.
The dicobalt methylidyne complex [{(C5HiPr4)Co}2(μ-CH)(μ-H)] (5) was obtained in high yield from the reaction of [(C5HiPr4)Co(μ-Cl)]2 (4) with two equivalents of methylmagnesium chloride. According to DFT calculations the dinuclear alkylidyne complexes 3 and 5 contain d6 metal centers, namely, iron(II) (3) and cobalt(III).
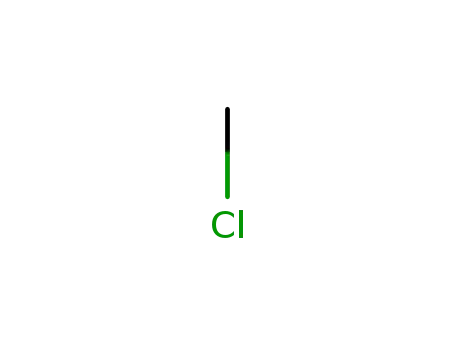
methylene chloride

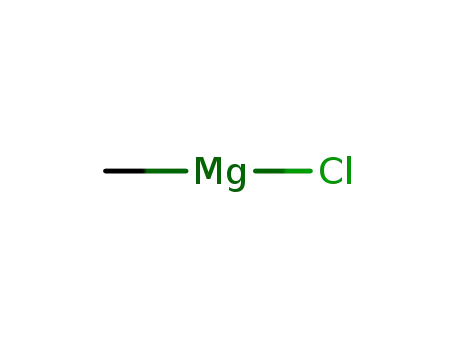
methylmagnesium chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With magnesium; In tetrahydrofuran;
|
|
|
With magnesium; In solid matrix; at -258.2 ℃;
|
|
|
With magnesium; lithium chloride; In tetrahydrofuran; at 0 - 20 ℃; Inert atmosphere;
|
|
|
With iodine; magnesium; In dibutyl ether; at 40 ℃; for 1h; Solvent; Inert atmosphere;
|

methylene chloride

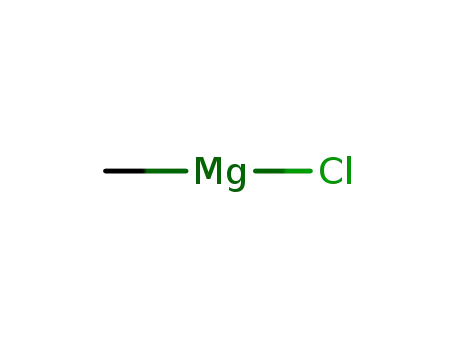
methylmagnesium chloride
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With diethyl ether;
|

methylene chloride
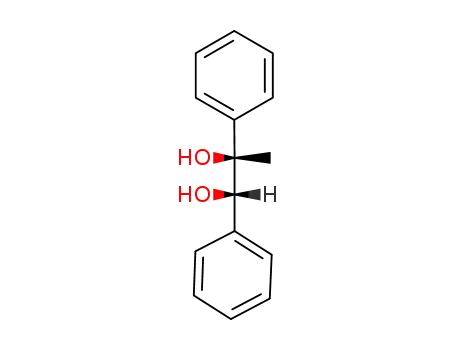
(1RS,2SR)-(+/-)-1,2-diphenyl-1,2-propandiol
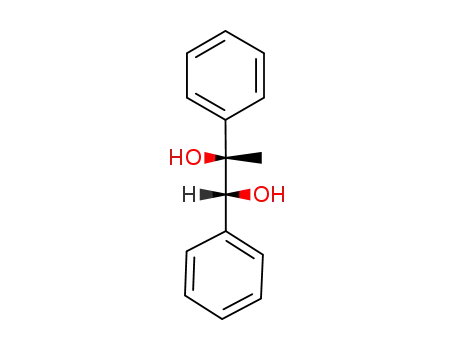
(1RS,2RS)-(+/-)-1,2-diphenyl-1,2-propandiol
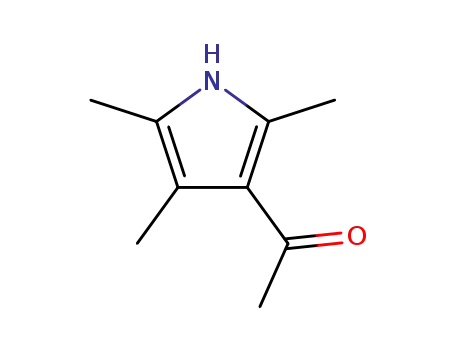
2,4,5-Trimethyl-3-acetyl-pyrrole
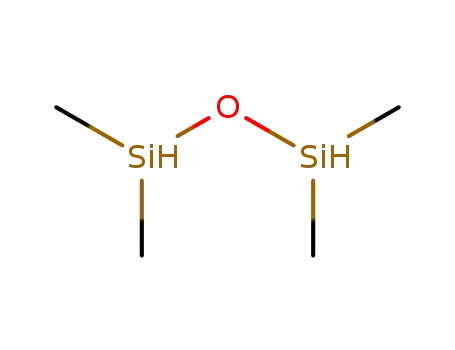
1,1,3,3-Tetramethyldisiloxane